DSBOARD-XV2 Serial Communication Interfaces Tutorial
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN?
ENVIRONMENT
In this blog post, we will look at the pinout diagram of I/O connector on DSBOARD-XV2. Then, we will install GTKTerm serial connection application. Finally, we will test the RS232, RS422 & RS485 connections.
The Pinout of I/O Connector
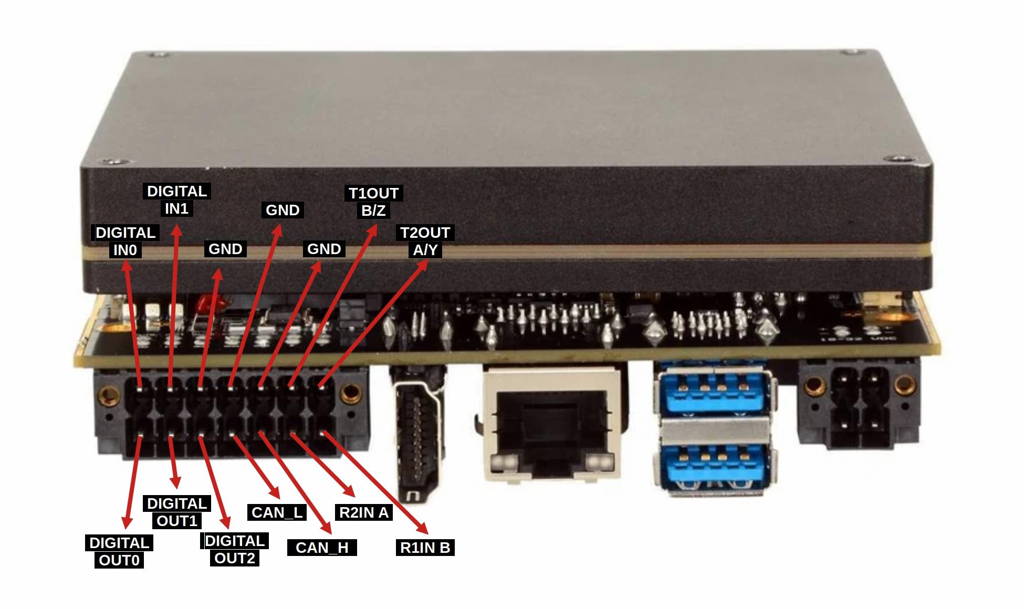
First, let's look over the IO connector. On the connector, there are 4 serial communication pins and 2 digital ground pins. When using a serial communication interface, you should always double-check which ground pin you are using. Also, use a digital ground for serial communication applications.
Installing GTKTerm
To test all serial communication interfaces, open a new terminal and install the GtkTerm program for ease of use (make sure Ethernet cable is connected). You can install GtkTerm with this terminal command:
sudo apt install gtkterm
Testing the Serial Communication Interfaces
Run the GtkTerm program with arguments. On the host side, you can use TeraTerm or Putty for Windows; GtkTerm for Ubuntu OS.
RS232 Test
To test RS232 functionality, we use a DSBOX-TX2NX as a test equipment. (If you use a USB-Serial adapter, connect that adapter to the USB port of the host PC and install its driver software if necessary.) To the other side of the connector, connect your device’s RS232 pins with cross-connection (Rx to Tx, Tx to Rx). You can find the hardware pins below. For ground connection, use GND_DIGITAL pin.
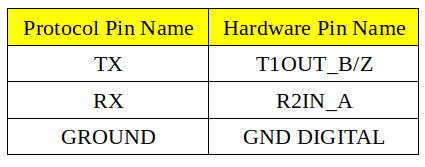
After proper connection, you should do pin multiplexing on your device to use serial port as RS232.
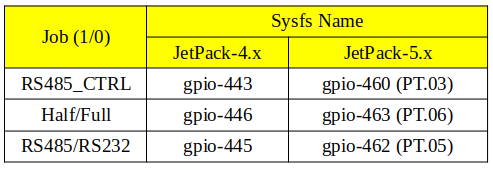
For JetPack-4.x
To do this, open new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 446 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 445 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/value"
For JetPack-5.x
Open a new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 463 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 462 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/value"
If you are using GtkTerm on Ubuntu, run these commands below. If you have done everything correctly you could see your keyboard presses on the other machine's serial terminal.
sudo gtkterm -p /dev/ttyTHS1 -s 115200
RS422 Test
To test RS422 functionality, we use a DSBOX-TX2NX as a test equipment. (If you use a USB-Serial adapter, connect that adapter to the USB port of the host PC and install its driver software if necessary.) To the other side of the connector, connect your device’s RS422 pins with cross-connection (Rx to Tx, Tx to Rx but positive to positive, negative to negative). You can find the hardware pins below. For ground connection, use GND_DIGITAL pin.
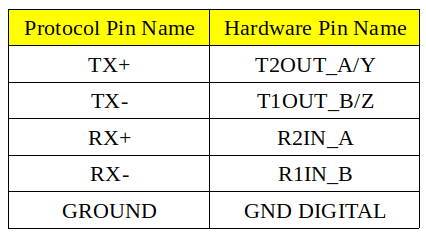
After proper connection, you should do pin multiplexing on your device to use serial port as RS422.
For JetPack-4.x
To do this, open new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 446 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 445 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/value"
For JetPack-5.x
Open a new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 463 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 462 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/value"
If you are using GtkTerm on Ubuntu, run these commands below. If you have done everything correctly you could see your keyboard presses on the other machine's serial terminal.
sudo gtkterm -p /dev/ttyTHS1 -s 115200
RS485 Test
To test RS485 functionality, we use a DSBOX-TX2NX as a test equipment. (If you use a USB-Serial adapter, connect that adapter to the USB port of the host PC and install its driver software if necessary.) To the other side of the connector, connect your device’s RS485 pins. You can find the hardware pins below. For ground connection, use the GND_DIGITAL pin.

After proper connection, you should do pin multiplexing on your device to use Serial Port as RS485.
For JetPack-4.x
To do this, open new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 443 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 446 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 445 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio443/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio446/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio445/value"
To write data:
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio443/value"
To read data:
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio443/value"
For JetPack-5.x
Open a new terminal then type these commands below.
sudo sh -c "echo 460 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 463 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo 462 > /sys/class/gpio/export"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.03/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo out > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/direction"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.06/value"
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.05/value"
To write data:
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.03/value"
To read data:
sudo sh -c "echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/PT.03/value"
If you are using GtkTerm on Ubuntu, run these commands below. If you have done everything correctly you could see your keyboard presses on the other machine's serial terminal.
sudo gtkterm -p /dev/ttyTHS1 -s 115200 -w RS485
Thank you for reading our blog post.


